The problem with the Regen radio was that it was fidgety and lacked selectivity. The next type of tube radio then was called the TRF for Tuned radio frequency.
The idea was a series of amplifiers each with a tuning coil. There were just too many tuners! But it can fine tune to a station. It was still figedty to the taste and something has to be developed to make a USER FRIENDLY radio. Armstgrong went back to the drawing board.
He knew the principle that frequencies can be MIXED. His goal was go reduce the number of tuning condensers. Finally, he invented the SUPERHETERODYNE radio when a local oscillator is mixed with the incoming signal. The tuning capacitors of the antenna coil and the oscillator coil were ganged. The differential frequency was kept constant at 455 Khz. The next amplifier as tightly tuned to 455 Khz. Till today, this principle is still used.
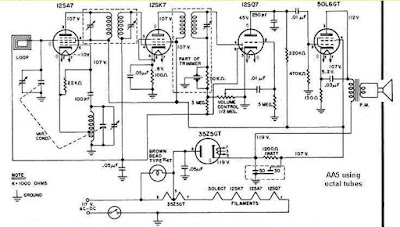
Superhets spread all over the world and in the U.S.A., the most common was a five tube set up. It was called the All American 5 or AA5. ?The firs tube was mixer-oscillator, the second tube was the IF amplifier, the 3rd tube was a diode-triode combo and finall the power amp. A fifth tube was the rectifier.
Comments
Post a Comment